SmmPanelUS API Architecture: Complete Integration Specification v2
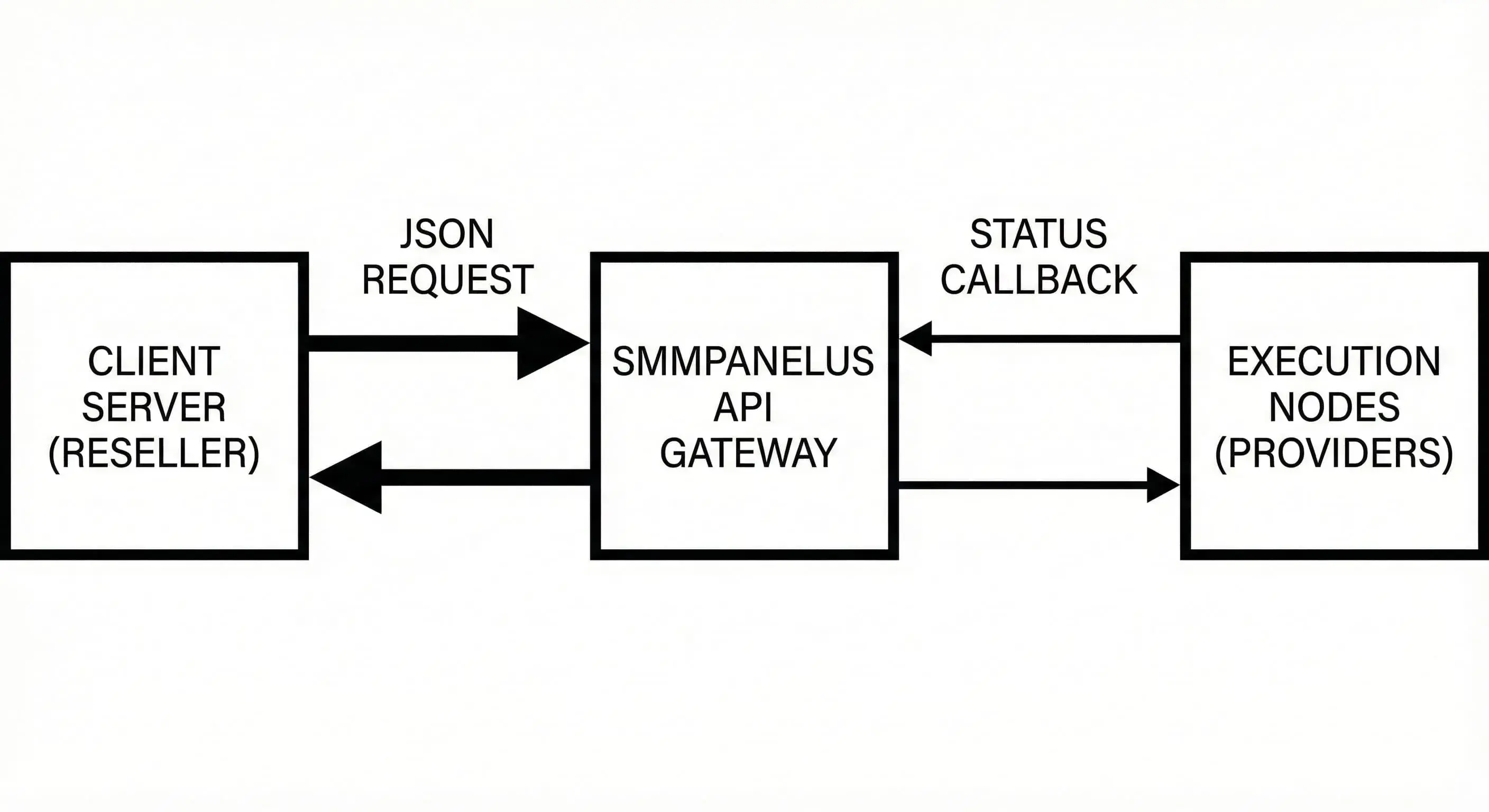
SmmPanelUS does not function as a standard agency. We operate as an Execution Layer. We accept standardized requests and distribute them to execution nodes. This is a transactional tool.
Integration requires strict adherence to Rate Limiting and data validation on the client side. Unlike the web interface, the API does not forgive syntax errors. Any violation of the data format triggers a Request Denial at the input filter level. This is an engineering instrument: you send a JSON payload, the system queues it, and the provider executes it.
Architectural Essence: Transactions are atomic. A request is either accepted and billed, or rejected. There are no intermediate states.
1. Basic Protocol and Authentication
Interaction occurs via HTTP POST requests to a single entry point. The architecture is not a classic RESTful service; it is RPC-over-HTTP. The `action` parameter determines all operations.
- Endpoint: `https://smmpanelus.com/api/v2`
- Content-Type: `application/json`
- Auth: The `key` parameter (Your API Token) is mandatory for every request.
2. Discovery: Retrieving Service Lists
Your system must know the current service IDs and parameters before creating an order. The `action=services` method returns the full catalog. We observe that caching this response (Redis/Memcached) with a TTL of at least 24 hours reduces latency significantly compared to querying it before every order.
// Request
{
"key": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"action": "services"
}
// Response Example
[
{
"service": 1,
"name": "Followers HQ",
"type": "Default",
"category": "Instagram",
"rate": "0.90", // Cost per 1000
"min": "50",
"max": "10000",
"refill": true, // Auto-refill availability
"cancel": true // Cancellation availability
}
]
Traffic Categorization (Routing Categories)
The `type` parameter defines the routing logic and required fields:
| Type | Purpose | Specifics |
|---|---|---|
| Default / Package | Standard queue. | Direct execution. |
| Custom Comments | User-defined comments. | Requires `comments` field (text separated by `\n` or array). |
| Mentions User Followers | Mentioning donor followers. | Requires link to post and donor `username`. |
| Poll | Poll voting. | Requires `answer_number`. |
3. Transaction: Order Creation
The `add` method initiates fund deduction and places the task in the queue.
Parameter Specification
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| `service` | integer | Service ID from the catalog. |
| `link` | string | Target URL. Validate for `https://` and no spaces. |
| `quantity` | integer | Amount. Strictly `>= min` and `<= max`. |
| `runs` (opt.) | integer | Number of executions (for Drip-feed). |
| `interval` (opt.) | integer | Pause in minutes between runs (for Drip-feed). |
Drip-feed Architecture
Use `runs` and `interval` to spread execution over time. The total order volume is calculated using the formula:
$$ TotalQuantity = Quantity \times Runs $$
// Response (Success)
{
"order": 23501 // Store this ID for tracking
}
4. Monitoring: Status and Lifecycle
Status checking is the most resource-intensive operation. Using a single `status` method inside a loop is an architectural error that often triggers WAF blocking.
Lifecycle States
- Pending: Order queued for provider submission.
- In progress: Provider accepted the order; execution active.
- Completed: Finished.
- Partial: Partial execution. Funds for the undelivered remainder (`remains`) returned to balance.
- Canceled: Order canceled; full refund issued.
- Processing: Intermediate processing state.
Multi-Status (Best Practice)
Use `action=multi_status` to pass up to 100 Order IDs separated by commas. This reduces network load by a factor of 100.
// Request
{
"key": "API_KEY",
"action": "multi_status",
"orders": "1, 10, 100"
}
// Response
{
"1": {
"charge": "0.27819",
"start_count": "3572", // Counter at start
"status": "Partial", // Partial execution
"remains": "157", // Remainder (funds refunded)
"currency": "USD"
},
"10": {
"error": "Incorrect order ID"
}
}
5. Advanced Lifecycle: Refill and Cancel
Managing complex states (restoration, cancellation) also supports bulk operations.
Multi-Refill
Creating refill tasks for a list of orders.
// Request
{
"key": "API_KEY",
"action": "multi_refill",
"orders": "1, 2, 3"
}
// Response
[
{
"order": 1,
"refill": 1 // Refill task ID
},
{
"order": 2,
"refill": { "error": "Incorrect order ID" }
},
{
"order": 3,
"refill": { "error": "Refill not available for this service" }
}
]
Multi-Cancel
Attempting bulk cancellation. Note: A successful request does not guarantee cancellation; it guarantees a cancellation attempt.
// Request
{
"key": "API_KEY",
"action": "cancel",
"orders": "1, 99"
}
// Response
[
{
"order": 1,
"cancel": 1 // Cancellation request accepted
},
{
"order": 99,
"cancel": { "error": "Order is already completed" }
}
]
6. Finance: Balance Check
Use the `balance` method for billing automation. We recommend calling this no more than once every 5-10 minutes or after a series of large orders.
// Request
{
"key": "API_KEY",
"action": "balance"
}
// Response
{
"balance": "100.84292",
"currency": "USD"
}
7. API Error Codes Reference (Troubleshooting Guide)
Errors are standard in distributed systems. Your client must handle them without crashing the pipeline. Server responses usually have HTTP Status 200 OK but contain an `error` field in the JSON body.
Error Code Table
| Error String | Symptom | Reason and Action |
|---|---|---|
| `Incorrect request` | Immediate Reject. | Reason: Wrong data type (string instead of int), missing mandatory fields (`link`, `quantity`). Action: Log payload before sending. |
| `Not enough funds` | Order not created. | Reason: Account balance is lower than order cost. Action: Configure Low Balance Alert. |
| `Service not found` | ID returns error. | Reason: Service disabled or ID changed. Action: Update service list via `services` method daily. |
| `Quantity too small/large` | Limit rejection. | Reason: `quantity` is outside `min`/`max` bounds. Action: Synchronize limits before sending. |
Code Pattern: Python Wrapper
Example of a robust implementation with timeout handling.
import requests
import json
class SmmPanelAPI:
def __init__(self, api_key, base_url="https://smmpanelus.com/api/v2"):
self.key = api_key
self.url = base_url
def _post(self, payload):
payload['key'] = self.key
try:
# Hard timeout: 5s connect, 30s read
response = requests.post(self.url, json=payload, timeout=(5, 30))
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
# Network error logging
print(f"Network Error: {e}")
return None
def add_order(self, service_id, link, quantity):
return self._post({
"action": "add",
"service": service_id,
"link": link,
"quantity": quantity
})
def get_multi_status(self, order_ids):
# order_ids -> list of integers
ids_str = ",".join(map(str, order_ids))
return self._post({
"action": "multi_status",
"orders": ids_str
})
8. Limitation of Liability
We provide the transport layer. We guarantee that a valid request will be accepted and transmitted to the execution network. However:
- We do not control the algorithms of the end platforms (Instagram, TikTok, etc.).
- We do not validate the quality of your links (private profiles or geo-blocks are client responsibilities).
- Execution speed depends on the current global gateway load.
9. FAQ: Technical Questions
Is the API idempotent?
No. The API does not support idempotency by default. If you send an `add` request twice with identical parameters, the system creates two different orders and deducts funds twice. Implement duplicate protection on your side (e.g., by generating unique Transaction IDs and checking them before sending).
What is the Gateway Rate Limit?
We do not publish hard numbers to prevent exploits, but the WAF blocks anomalous activity. The recommended status polling frequency is once every 15-20 minutes (using `multi_status`). Single requests more frequent than once per second may trigger a temporary IP ban.
Is this a RESTful API?
Technically, no. This is a JSON-RPC architecture over HTTP. We use one URL for all operations, and the action type is defined by the `action` parameter in the request body, not the HTTP method.
Is it safe to Retry on network error?
Only if you did not receive a server response (timeout). If you received any response (even 5xx or JSON with error), resending without checking the order status may lead to duplication. Check the latest orders via `action=status` first.
This document is a technical specification. Financial results depend on the business logic configuration on the partner's side.

